고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
728x90
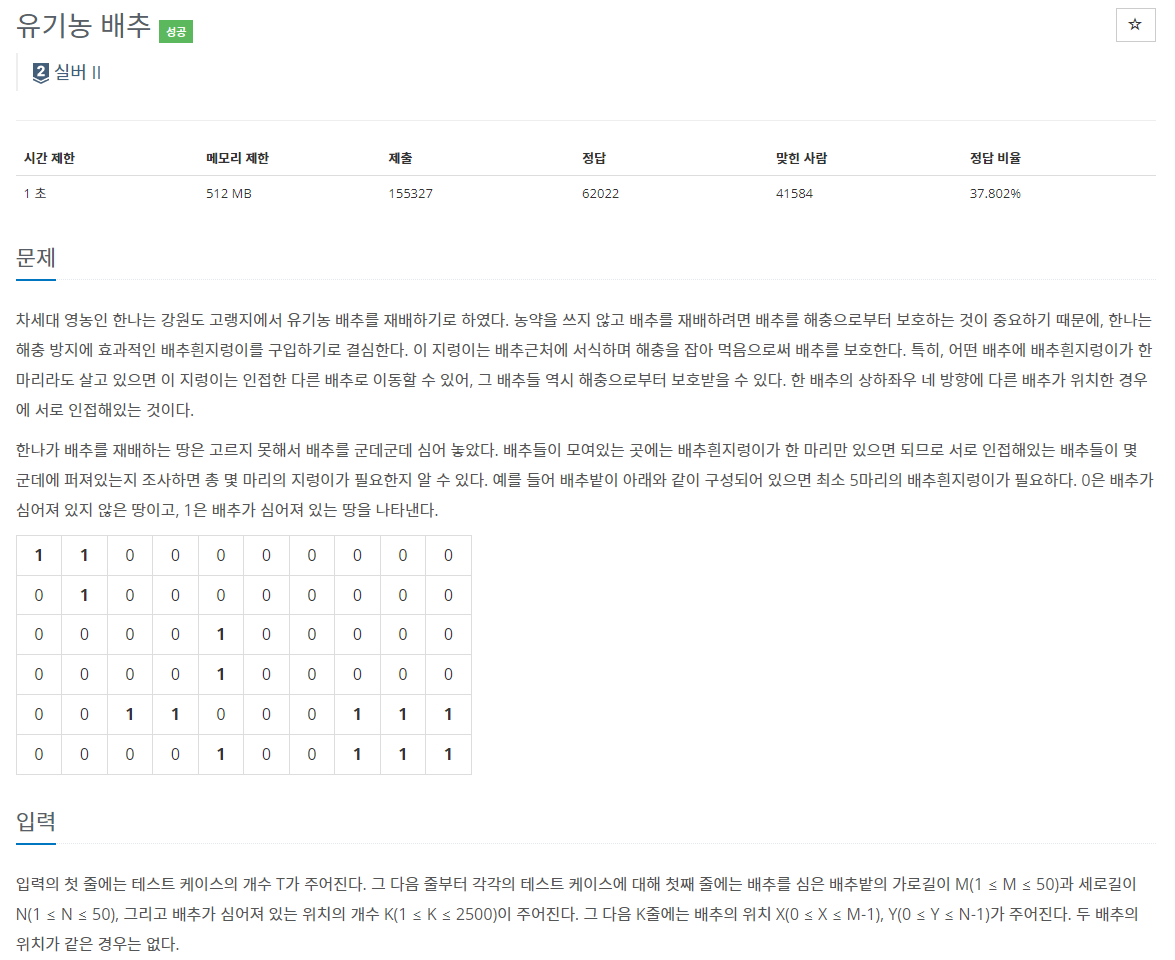
package com.dofury.kotlin
import java.io.BufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedWriter
import java.io.InputStreamReader
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter
class Location(val x: Int,val y:Int){
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (other !is Location) return false
return this.x == other.x && this.y == other.y
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
var result = x
result = 31 * result + y
return result
}
}
fun main() {
val br = BufferedReader(InputStreamReader(System.`in`))
val bw = BufferedWriter(OutputStreamWriter(System.`out`))
val T = br.readLine().toInt()
repeat(T){
val (m, n, K) = br.readLine().split(' ').map { it.toInt() }
val field = Array(m) {
Array(n) {
0
}
}
val cabbages = mutableListOf<Location>()
repeat(K){
val (x, y) = br.readLine().split(' ').map { it.toInt() }
cabbages.add(Location(x,y))
field[x][y] = 1
}
bw.write(bfs(field,cabbages).toString())
bw.newLine()
}
bw.flush()
bw.close()
br.close()
}
fun bfs(field: Array<Array<Int>>, cabbages: MutableList<Location>): Int {
val queue = ArrayDeque<Location>(1000)
val dx = intArrayOf(1, 0, -1, 0) // 오른쪽, 아래쪽, 왼쪽, 위쪽
val dy = intArrayOf(0, 1, 0, -1)
var count = 0
while (cabbages.isNotEmpty()) {
val startPoint = cabbages.removeAt(0)
if (field[startPoint.x][startPoint.y] == 1) {
queue.addLast(startPoint)
field[startPoint.x][startPoint.y] = 0 // 방문 처리
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val point = queue.removeFirst()
for (i in 0 until 4) {
val nx = point.x + dx[i]
val ny = point.y + dy[i]
if (nx in field.indices && ny in 0 until field[0].size && field[nx][ny] == 1) {// 상하 좌우 이동 및 배추인 경우
queue.addLast(Location(nx, ny))
field[nx][ny] = 0 // 방문 처리
}
}
}
count++
}
}
return count
}BFS를 활용하여 탐색을 시도하되, 배추가 있는 영역부터 탐색을 시작하였다.
허나 이미 탐색을 한 배추를 탐색할 수 있어서 배추가 담겨있는 LIST에서 REMOVE를 하여 구현 하였는데,
이렇게 할 시 시간 초과가 되어, 탐색한 배추는 field 변수에서 배추가 없는것과 동일하게 0으로 변경하여 해결할 수 있었다.
728x90
'코딩테스트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 바이러스(백준) (0) | 2023.07.28 |
|---|---|
| 계단 오르기(백준) (0) | 2023.07.27 |
| 케빈 베이컨의 6단계 법칙 (0) | 2023.07.25 |
| 덱(백준) (0) | 2023.07.24 |
| 큐(백준) (0) | 2023.07.23 |





댓글 영역